LLC student z table score [Expert Answers]
Table of Contents
- How do you find the z-score from a table?
- How do you find a 1.96 Z table?
- What is the probability where p (- 2.58 z 2.58 )?
- What is the z-score for 99 %?
- What is the z-score of 98%?
- Why is Z 1.96 at 95 confidence?
- What does a 1.96 z-score mean?
- How do I calculate 95% confidence interval?
- What is the z-score for 94 confidence interval?
- How do you find 0.025 in a Z table?
- What is a good z-score?
- What z-score is the top 5%?
- What if z-score is greater than 3?
- What is the z-score for 95%?
- What is the z-score for a 95 confidence interval?
- What is the z-score of 80%?
- What is the highest z-score?
- What is the z-score 10%?
- What is the minimum z-score?
- How do you interpret z-score?
Last updated : Aug 20, 2022
Written by : Santana Burts |
Current |
Write a comment |
How do you find the z-score from a table?
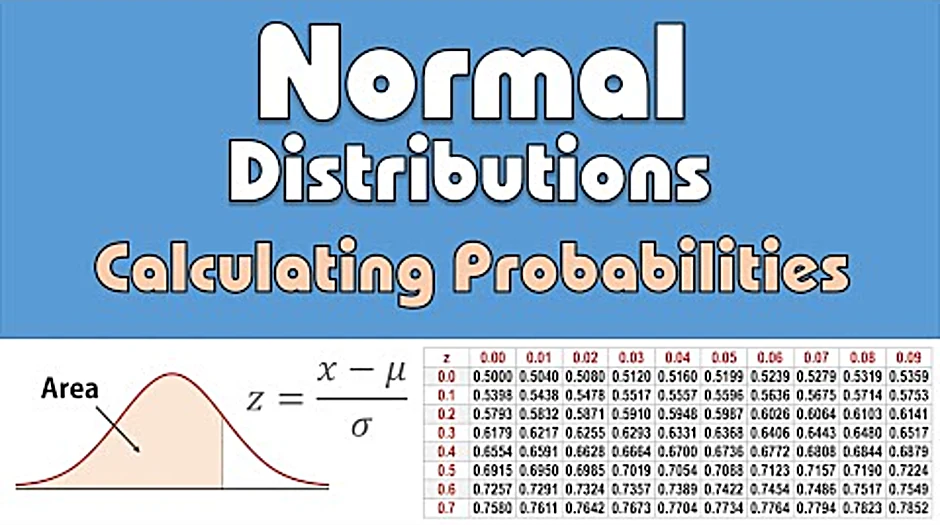
First, look at the left side column of the z-table to find the value corresponding to one decimal place of the z-score (e.g. whole number and the first digit after the decimal point). In this case it is 1.0. Then, we look up a remaining number across the table (on the top) which is 0.09 in our example. Figure 2.
What z-score is the top 5%?
“Top 5%†means the minimum percentile rank is at 95, which is 0.95 in percentage. Find out the corresponding z-score according to the percentile : There's no “0.95†in z-table but “0.9495†& “0.9505†Since the “minimum percentile` is 0.95, so “0.9505†is the one.
What is the z-score for 95%?
The critical z-score values when using a 95 percent confidence level are -1.96 and +1.96 standard deviations. The uncorrected p-value associated with a 95 percent confidence level is 0.05.
What is the z-score for a 95 confidence interval?
The value of z* for a confidence level of 95% is 1.96. After putting the value of z*, the population standard deviation, and the sample size into the equation, a margin of error of 3.92 is found. The formulas for the confidence interval and margin of error can be combined into one formula.
What is the z-score of 80%?
For example, the z* value for an 80% confidence level is 1.28 and the z* value for a 99% confidence level is 2.58.
What is the highest z-score?
Z-scores range from -3 standard deviations (which would fall to the far left of the normal distribution curve) up to +3 standard deviations (which would fall to the far right of the normal distribution curve).
What is the z-score 10%?
A z score of 1.282 separates the top 10% of the z distribution from the bottom 90%.
What is the minimum z-score?
Z-scores can take on any value between −∞ to ∞ , but when considering the empirical rule it is highly unlikely that they will go beyond -3 and 3. This is a common "minimum" and "maximum" used when considering the range of possible values in a distribution. For a more complete range, some will use -6 to 6.
How do you interpret z-score?
How do you interpret a z-score? The value of the z-score tells you how many standard deviations you are away from the mean. If a z-score is equal to 0, it is on the mean. A positive z-score indicates the raw score is higher than the mean average.
How do you find a 1.96 Z table?
The table value for Z is the value of the cumulative normal distribution. For example, the value for 1.96 is P(Z<1.96) = . 9750. 1.
What is the probability where p (- 2.58 z 2.58 )?
We only need one number: when z = -2.58 and we can do some math to get the final answer. The table says that the P( z<−2.58 ) = . 0049 or 0.49%.
What is the z-score for 99 %?
What is the Z-score for a 99% confidence interval? The z-score for a two-sided 99% confidence interval is 2.807, which is the 99.5-th quantile of the standard normal distribution N(0,1) .
What is the z-score of 98%?
Since you desire the 98% percent interval you desire 1% on each side of ±z , look up 99% (0.99) for z to obtain this. The closest value for 0.99 on the table gives z=2.32 on the table (2.33 in Excel), this is your z score.
Why is Z 1.96 at 95 confidence?
The value of 1.96 is based on the fact that 95% of the area of a normal distribution is within 1.96 standard deviations of the mean; 12 is the standard error of the mean.
What does a 1.96 z-score mean?
In probability and statistics, the 97.5th percentile point of the standard normal distribution is a number commonly used for statistical calculations. The approximate value of this number is 1.96, meaning that 95% of the area under a normal curve lies within approximately 1.96 standard deviations of the mean.
How do I calculate 95% confidence interval?
Calculating a C% confidence interval with the Normal approximation. ˉx±zs√n, where the value of z is appropriate for the confidence level. For a 95% confidence interval, we use z=1.96, while for a 90% confidence interval, for example, we use z=1.64.
What is the z-score for 94 confidence interval?
The z value associated with the 94% level of confidence is a 2.575, B 1.96, C 1.645, or D 2.33, Or E 1.88. at 94% confidence level, the Z is Alpha equals 1 -94%, which equals 1 -0.94, which gives us 0.06.
How do you find 0.025 in a Z table?
The right tail value, z (0.025), is found using Table 4, Part A, One-Tailed Situations, as shown previously. z(0.025) = 1.96, and since the standard normal distribution is symmetrical, the value of z(0.975) = –z(0.025) = –1.96. You can use two tails to find the area as well.
What is a good z-score?
According to the Percentile to Z-Score Calculator, the z-score that corresponds to the 90th percentile is 1.2816. Thus, any student who receives a z-score greater than or equal to 1.2816 would be considered a “good†z-score.
What if z-score is greater than 3?
A positive z-score says the data point is above average. A negative z-score says the data point is below average. A z-score close to 0 says the data point is close to average. A data point can be considered unusual if its z-score is above 3 or below −3 .

Check these related keywords for more interesting articles :
How to start a business LLC in arizona
Long leg cast LLC application
Free printable llc operating agreement
Who needs to get an LLC
Should i have an LLC for my airbnb experiences
How long to keep tax records for LLC
How to check llc business credit
What type of company is pershing LLC
LLC annual report west virginia
Can LLC write off vehicle business
Does an llc have to pay franchise tax
Free llc filing in wisconsin can you drink
Best llc service mileage reimbursement
Does an llc require a general partner
Which is better llp or LLC
Did you find this article relevant to what you were looking for?
Write a comment
Comment by Errol Mcdavid
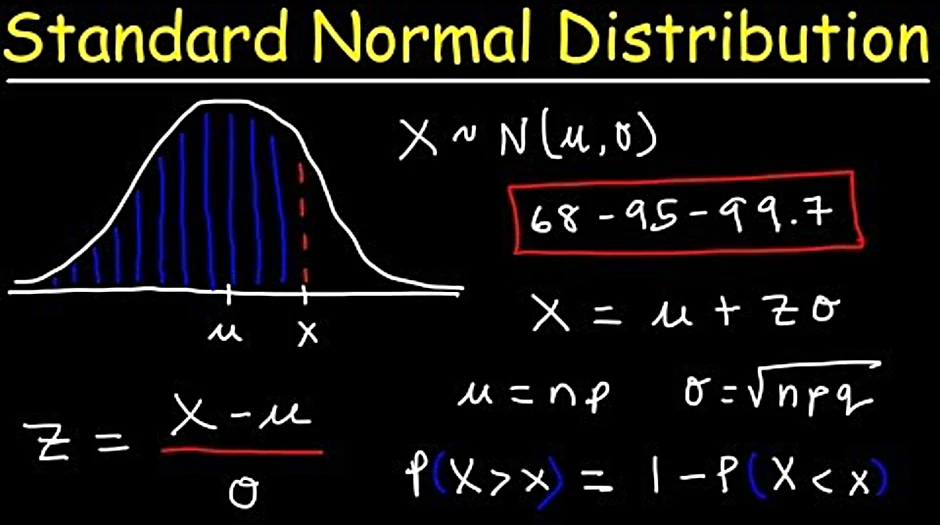
welcome in this video I'll be showing how to use the standard normal tables to calculate probabilities in a normal distribution a normal distribution is a symmetric bell-shaped distribution where the area under the normal curve is 100% the standard normal distribution or what is also called the Z distribution is a special normal distribution with a mean mu of 0 and a standard deviation Sigma of 1 the formula for transforming a score or observation X from any normal distribution to the standard normal score is Z equals X minus mu over Sigma the standard normal score also known as the z-score or Z value is the number of standard deviations a score X is from the mean the standard normal tables we will be using are the less than cumulative tables they usually have the left tail of the distribution shaded and also have positive and negative parts let's look at an example scores on an exam are normally distributed with a mean of 65 and a standard deviation of 9 we want to find the percent of scores satisfying a B and C here in a we want the probability that X is less than 54 so for x equals 54 the corresponding z-score is 54 minus 65 divided by 9 and that gives negative one point two two two two repeating since the Z table is set up to handle only two decimal places where round is to negative one point two two we then go to the Z table and look up the area for Z equals negative one point two two we go to the negative side of the table look for negative one point two in the first column and point zero two at the top the corresponding area here is point one one one two that is the area to the left of Z equals negative one point two two is points 1 1 1 2 so on this normal curve for Z equals negative 1.2 to the area on the left here is point 1 1 1 2 as seen on the table therefore the probability that X is less than 54 is the probability that Z is less than negative 1 point 2 2 which gives point 1 1 1 2 or 11.1 2 percent in B we want the probability that X is at least 80 in continuous distributions like the normal distribution there is no distinction between X is at least 80 and X is greater than 80 we apply the same approach in both cases so for x equals ad Z equals 80 minus 65 divided by 9 and that gives 1 point 6 7 to 2 decimal places when we look that up in the Z table by checking one point six on the point zero seven we find point nine five two five which is the area to the left of Z here we then subtract it from 1 to obtain the greater than area since the total area under the curve is 1 therefore the probability that X is at least 80 is the probability that Z is greater than one point 6 7 which equals one minus point nine five two five giving point zero 4 7 5 or four point seven five percent in C we want the probability that X is between 70 and 86 for x equals 7t z equals point five six and for x equals 86 z equals two point three three on the table the area less than Z equals two point three three eight point nine nine zero one while the area less than Z equals point five six is point seven one two three when finding the area between two Z values from the cumulative less than tables we subtract the smaller area from the larger one so the probability that X is between 70 and 86 is the probability that Z is between point five six and two point three three that is 0.99 zero one minus point seven one two three which gives point two seven seven eight or twenty seven point seven eight percent in summary if you're finding a less than area using the cumulative less than tables the area in the table is the answer if you want a greater than area then do one minus the area from the table and if you want the area between two Z values then do bigger area which will correspond to the larger Z value minus the smaller area which will correspond to the smaller Z value note that we do not subtract Z values we only subtract areas and that concludes this video thanks for watching
Thanks for your comment Errol Mcdavid, have a nice day.
- Santana Burts, Staff Member
Comment by hottie92988U
in this video we're gonna go over the standard normal distribution as well as some equations that you need to be familiar with after that we're gonna work on some problems so you could see how to put these formulas to good use so the normal distribution has the shape of a bell curve it looks something like that now the notation for it perhaps you've seen this in your book is the random variable X so for a normal distribution you have two important parameters that you need to know that is the mean and the standard deviation represented by the symbol Sigma that kind of looks like Fayette Emma there it is now the mean is right in the middle of the bell curve and here this would be one standard deviation from the mean and over here this will be about one standard deviation away from the mean on the left side the z-score that corresponds to one standard deviation is simply one when X is less than the mean the z-scores are negative so two standard deviations away from the mean z is equal to two on the left side Z is going to be negative two and let's say over here this is three Stevi a shion's from the mean so Z is going to be three and the same is true for the other side now the formula that you need in order to calculate the z-score is this Z that's a terrible looking Z let's do that again Z is equal to X minus the mean divided by the standard deviation sometimes you may need to calculate X X is equal to the mean plus Z times the standard deviation so these are some formulas that you want to make sure you write down for the problems that I'm going to give you later the probability density function for a normal distribution is this function here f of X is equal to 1 divided by the standard deviation times the square root of 2 pi times e raised to the negative 1/2 times X minus the mean divided by the standard deviation squared now keep in mind e is a number it's approximately 2.718 something this continues now in the regular statistics class you won't need this formula you just need to know that it is the PDF or the probability density function for the normal distribution but you really don't need to use it in order to calculate the answer unless you're using it with calculus or something it does involve integral calculus to calculate the probabilities with that formula I've actually did that in another video on YouTube you could find it it was probably posted about a year ago or something if you want to know how to use calculus to get the answer but for this particular video we're not going to go into that much detail but just in case you see a question on a test at least you know that this formula corresponds to the normal distribution now there's something called the empirical rule that you need to be familiar with so the empirical rule tells us that 68% of the x values lie within one standard deviation of the mean ninety-five percent of the x values lie within two standard deviations of the mean and ninety-nine point seven percent of the x values lie within three standard deviations of the mean so knowing that how would you calculate the area under the curve expressed as a percentage in each of these sections well if this area here is 68% if we divide that by two that means this region must be thirty-four percent as well as the left side as well now what is the area in terms of excuse me in terms of a percent for those two regions to get that answer you need to subtract these two numbers 95 minus 68 that's gonna give us 27 and then if you divide that by 2 you're gonna get 13.5 now it's important to understand that the area of a continuous probability distribution function is 1 so the area of this region is gonna be a decimal value it's 0.135 the same is true for this region here so keep that in mind a total area under the curve is equal to one now what is the probability of finding an x value in those two regions so what we need to do is subtract those two numbers and ninety-nine point seven minus 95 that's going to give us four point seven and then divide that by two so you should get two point three five percent that's the probability of finding or get an x value in that region now the remaining portions by the way this should be like very close to the x-axis my drawing wasn't perfect but to find the remaining part it's going to be a hundred minus nine nine point seven which is 0.3 divide that by two and so there's a point fifteen percent chance of finding and or of getting an x value beyond three standard deviations so those are the values when using the empirical rule to solve probability questions relating to the normal distribution we're going to talk about how to use this chart later in this video but feel free to write down this information because it's going to be useful shortly so here's the first example problem that we're going to work on in this video now for each of these problems feel free to pause the video if you want to try it yourself before seeing the answer and when you want to check your answer just play the video to see if you got it so let's begin so given this information here what are the values of the mean and standard deviation so what you need to know is that the first number corresponds to the mean the second number corresponds to the standard deviation so the mean is 50 in this example and a standard deviation is 10 now Part B and what value of x has a z-score of 1.4 so if Z is equal to 1.4 what is the value of X what do you think we need to do what formulas should we use so perhaps you wrote down this formula X is equal to the mean plus Z times the standard deviation so the mean is 50 the z-score is 1.4 and the standard deviation is 10 now 1.4 times 10 is 14 and 50 plus 14 and that's going to give us 64 so this is the answer for Part B so that's how you can calculate x given the value of Z now what about Part C what is the z-score that corresponds to a value I mean that corresponds to x equals 30 so if X is 30 what is Z so now we're going to use the rearranged formed let me excuse me the rearranged form of that formula so here it is the z-score is X minus the mean divided by the standard deviation so X is 30 the mean is 50 and the standard deviation is 10 so 30 minus 50 is negative 20 20 divided by 10 is 2 so negative 20 divided by 10 is negative 2 so that's the answer for Part C now let's move on to Part D what is the difference between positive and negative Z values let's create a number line and let's put the mean in the middle now when X was 64 this correspond to a z value of positive 1.4 and when X was 30 the Z value that it corresponded to was negative 2 so as you can see negative Z values are below the mean they correspond to X values that are below the mean and positive z values correspond to X values that are above the mean and so that's really the difference between positive and negative Z values the negative Z values are going to be to the left of the mean and the positive z values will be towards the right of me now let's move on to the next problem the average test score in a certain statistics class was 74 with a standard deviation of 8 there are 2,000 students in this class use the empir
Thanks hottie92988U your participation is very much appreciated
- Santana Burts
About the author

Santana Burts
I've studied problem solving at Chaminade University of Honolulu in Honolulu and I am an expert in limnology. I usually feel sad. My previous job was environmental technician I held this position for 20 years, I love talking about cycling and caving. Huge fan of Jessica Alba I practice hacky sack and collect books.
Try Not to laugh !
Joke resides here...
Tags
How do you find a 1.96 Z table
What is the probability where p - 2.58 z 2.58
What is the z-score for 99
What is the z-score of 98
Why is Z 1.96 at 95 confidence
What does a 1.96 z-score mean
How do I calculate 95 confidence interval
What is the z-score for 94 confidence interval
How do you find 0.025 in a Z table
What is a good z-score
What z-score is the top 5
What if z-score is greater than 3
What is the z-score for 95
What is the z-score for a 95 confidence interval
What is the z-score of 80
What is the highest z-score
What is the z-score 10
What is the minimum z-score
How do you interpret z-score
 : 2031
: 2031